Lassa fever or Lassa hemorrhagic fever (LHF) is an acute viral hemorrhagic fever caused by the Lassa virus and first described in 1969 in the town of Lassa, in Borno State, Nigeria. Lassa fever is a member of the Arenaviridaevirus family. Similar to ebola, clinical cases of the disease had been known for over a decade, but had not been connected with a viral pathogen.
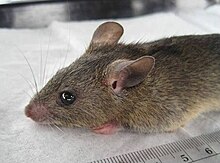
Lassa frequently infects people in West Africa. It results in 300,000 to 500,000 cases annually and causes about 5,000 deaths each year. Outbreaks of the disease have been observed in Nigeria, Liberia, Sierra Leone, Guinea, and theCentral African Republic. The primary animal host of the Lassa virus is the Natal multimammate mouse (Mastomys natalensis), an animal found in most of sub-Saharan Africa. The virus is probably transmitted by contact with the feces or urine of animals accessing grain stores in residences. Given its high rate of incidence, Lassa fever is a major problem in affected countriesRecently cases of this disease came up in Rivers STATE. As a matter of fact this disease can be controlled if necessary sanitation is kept in the neighbourhood. This disease stay within the tissue between 6 to 22 day before manifesting. Some of the signs includes vomiting blood, diarrhea blood, stomach ache, difficulty swallowing among others.
TRANSMISSION:
This disease is transmitted by rat. The very common one that runs around in the house. read what wikipedia has to say again.
Lassa fever is spread to humans from rodents, specifically multimammate mice (Mastomys natalensis). This is probably the most common mouse in equatorial Africa, ubiquitous in human households and eaten as a delicacy in some areas. The virus is shed in their excreta (urine and feces), which can be aerosolized. In fatal cases, Lassa fever is characterized by impaired or delayed cellular immunity.
Infection in humans typically occurs by exposure to animal excrement through the respiratory or gastrointestinal tracts. Inhalation of tiny particles of infectious material (aerosol) is believed to be the most significant means of exposure. It is possible to acquire the infection through broken skin or mucous membranes that are directly exposed to infectious material. Transmission from person to person has also been established, presenting a disease risk for healthcare workers. Frequency of transmission by sexual contact has not been establishedProtecting ourselves from this deadly animal could be and easy way to protect ourselves from the deadly disease called Lasser fever..
No comments:
Post a Comment